DRINK YOUNG AND CRASH (DomPost, 28 December 2005) New Zealand's decision to lower the drinking age to 18 has resulted in an alarming increase in teenage car smashes, a landmark American study says. Alcohol was linked to "significantly more" vehicle crashes among 15 to 19-year-olds since the law was changed in 1999 to allow 18-year-olds to buy booze, the American Journal of Public Health says in an article to be published next month. ... [full article, pdf]See also:
- “Crashes Blamed on Law Change” (The Press, 28 December 2005) [pdf]
- “Sobering news for Kiwi culture” (DomPost, 28 December 2005) [pdf]
As an aside, it wasn’t really “new” news; the NZ Herald reported the results about 3 months earlier – under a more alarming headline:
LOW DRINK AGE KILLS 12 TEENS A YEAR (NZ Herald, 8 September 2005) Lowering the drinking age to 18 has cost the lives of 12 teenagers each year in New Zealand and is putting more than 400 in hospital with traffic related injuries, new research suggests. ... [full article, pdf]Now, when applying a harm-based justification for criminalisation, this research seems to be death knell for the lower drinking age. The study suggests decriminalisation produces measured, significant harm. Unsurprisingly, proponents of raising the drinking age latched onto the research and championed their Amendment Bill.
The results of the research seems so concerning I thought it necessary to read the journal article itself.
- See K Kypri et al, “Minimum Purchasing Age for Alcohol and Traffic Crash Injuries Among 15- to 19-Year-Olds in New Zealand” (2006) 96 American Journal of Public Health 126 [pdf]
And yes, the article did conclude as follows:
Conclusions: Significantly more alcohol-involved crashes occurred among 15- to 19-year-olds than would have occurred had the purchase age not been reduced to 18 years. The effect size for 18- to 19-year-olds is remarkable given the legal exceptions to the pre-1999 law and its poor enforcement.Given the conclusion and the press reports above, it may surprise you that the study actually showed that, in absolute terms, the rate of alcohol related crash injuries for 18- to 19-year olds actually dropped following the lowering of the drinking age (by about 7%).
The rate of alcohol related crash injuries for 18- to 19-year olds per 10,000 population was 215.4 for 1995-1999 compared with 199.6 for 1999-2003.
Similarly, rate of hospitalisations for (all) traffic crashes for 18-year olds fell (282.6 vs 201.9 or a drop of around 30%).
The 2 sets of reports data are shown in the following tables:
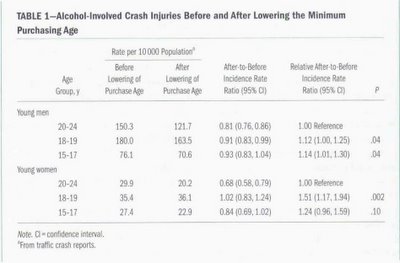
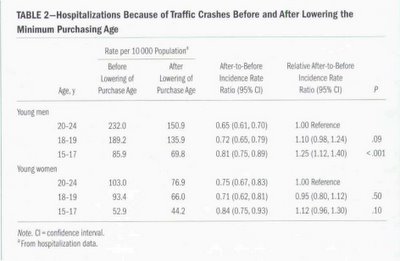 Of course, I’m no scientist or statistician (and I invite comment from such folk), but from what I can discern the explanation is that the study looked at relative, not absolute rates of injuries and hospitalisations. That is, when compared to a control group (20-24-year olds), the rates of injuries and hospitalisations for 18- to 19-year olds did not fall as much over the periods. The authors explain it as follows:
Of course, I’m no scientist or statistician (and I invite comment from such folk), but from what I can discern the explanation is that the study looked at relative, not absolute rates of injuries and hospitalisations. That is, when compared to a control group (20-24-year olds), the rates of injuries and hospitalisations for 18- to 19-year olds did not fall as much over the periods. The authors explain it as follows:
The rationale for including the 20- to 24-year age group was to control for the trend in crash outcomes that would have occurred irrespective of the change in minimum purchase age. In the period of the study, those aged 20 to 24 years were probably exposed to equivalent economic enforcement conditions, police enforcement levels, and other alcohol availability variables that may have influenced road traffic crashes in the younger age groups.Now, that does seem to make sense, particularly when scientifically trying to identify the sole effect of lowering the drinking age. However, I do think the headlines and analysis seem to belie the data when placed in the context of the present debate.
First, the data is being reported as if injuries and hospitalisations have increased in an absolute sense (any reference to comparative results in the press articles was, at best, oblique).
Secondly, I’m not convinced the use of relative data is necessarily appropriate for this present debate. Law reform such as lowering the age does not happen in a vacuum. The lowering of the age was combined with other messages to ameliorate problems associated with drinking. Surely those other contextual factors and corresponding results are relevant to the present debate.
Thirdly, even when seen in relative terms, I’m also not convinced the relative rates (overall, for men and women combined, I think around 18%), speak decisively in favour of raising the age. Undoubtedly there are costs associated with lowering the age. It is not surprising that allowing 18- to 19-year olds has lead to increased alcohol related incidents anyway – consumption of alcohol by any age group surely leads to alcohol related incidents.
Isn’t the better question to ask whether that relative increase is an appropriate cost of the liberty interest at stake? And is the relative cost any higher than for any other age group? Would a similar study of 20- to 24-year compared to 25-29 year olds demonstrate a similar relative cost? What influence does our driving registration system have on the results? Does the fact that our 18- to 19-years olds are obtaining full licences have any effect? Would these results be different if, for example, we raised the (initial) driving age to say 18 years with full licences obtained at 20 years?
In short, I think the study raises more questions than it answers (or fails to answer some of the important jurisprudential/political questions). Having read the study I am unpersuaded. I still intuitively feel that 18 is the appropriate benchmark for the transformation of youths into adults. I think a much stronger case needs to be made to justify any age-based restrictions for people older than 18.




3 comments:
Interesting blog.
It's too bad it seems like no one has read it.
I'd want to see some research into correlation with the increasing availability of cheap powerful cars...
Or a correlation with cheap beer and liquor--maybe the alcohol taxes need a hike? The lower the drinking age, the more price-sensitive young drinkers are. Just a thought.
Post a Comment